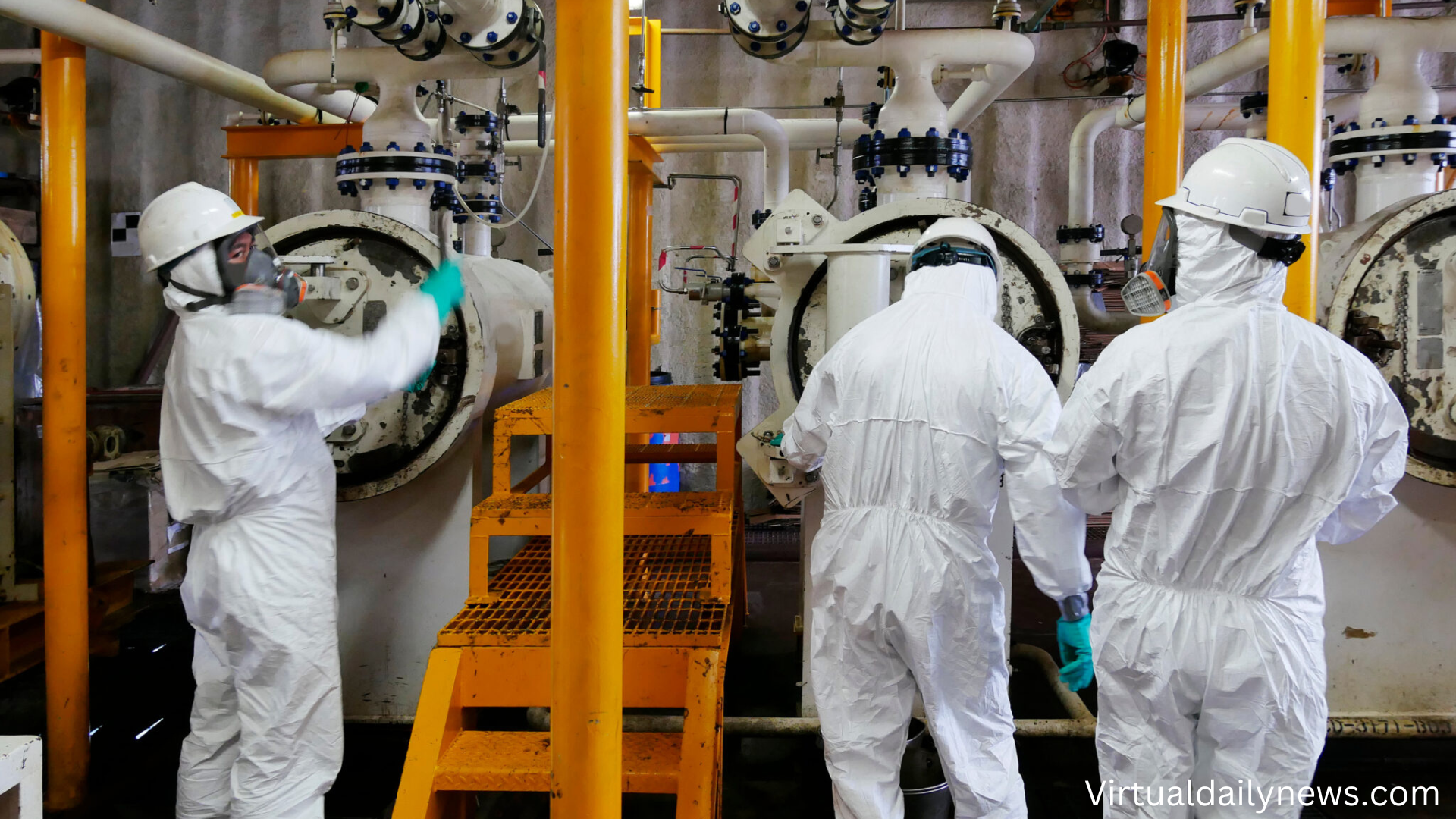
The US government is facing significant hurdles in rehiring nuclear safety personnel after a controversial decision to lay off key employees. The National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA) and the Department of Energy (DOE) are struggling to bring back essential staff who oversee the nation’s nuclear security. This article delves into the challenges, causes, and potential consequences of these layoffs, as well as the broader implications for national security.
The Importance of Nuclear Safety
Nuclear safety is a critical component of national security, ensuring the proper handling, storage, and maintenance of nuclear materials. The personnel in charge of these duties are highly specialized professionals responsible for preventing atomic accidents, maintaining weapons stockpiles, and overseeing nuclear facilities.
Key Responsibilities of Nuclear Safety Personnel
- Maintaining Nuclear Stockpiles: Ensuring that nuclear weapons remain secure and operational.
- Overseeing Nuclear Facilities: Monitoring atomic reactors and research facilities for safety compliance.
- Preventing Nuclear Accidents: Implementing protocols to reduce the risk of hazardous incidents.
- Handling Radioactive Materials: Managing and disposing of nuclear waste safely.
Why Were Nuclear Safety Employees Laid Off?
The recent layoffs of nuclear safety personnel were part of a broader effort by the government to reduce federal spending and streamline the workforce. However, this decision has sparked widespread concerns over national security risks and operational inefficiencies.
Factors Behind the Layoffs
- Cost-Cutting Measures: The administration aimed to reduce federal expenses, impacting multiple agencies, including the NNSA.
- Government Downsizing: A broader strategy to reduce the number of federal employees across various departments.
- Policy Shifts: Changes in national priorities led to restructuring within the energy sector.
- Automation and AI: Increased reliance on technology and automation to replace some human roles.
The Challenge of Rehiring Laid-Off Staff
After realizing the critical nature of nuclear safety roles, the government is now attempting to rehire many of the laid-off employees. However, the process is proving difficult for several reasons.
Key Challenges in Rehiring
- Lack of Communication: Many former employees were not adequately informed about the rehiring process.
- Loss of Trust: Employees who were laid off may be reluctant to return due to job security concerns.
- Competitive Job Market: Many professionals have already secured jobs elsewhere.
- Security Clearance Issues: Rehiring personnel requires updated security clearances, which can take time.
Impact on National Security
The sudden reduction in nuclear safety personnel has raised grave national security concerns. A shortage of trained professionals in nuclear facilities increases the risk of operational inefficiencies and safety breaches.
Potential Consequences
- Increased Safety Risks: Without sufficient oversight, the chances of accidents or security threats rise.
- Delays in Nuclear Programs: The maintenance and modernization of nuclear weapons may face setbacks.
- Loss of Expertise: The departure of experienced personnel creates a knowledge gap that is difficult to fill.
- Regulatory Compliance Issues: Reduced staff can lead to non-compliance with nuclear safety regulations.
The Role of Private Sector and Technology
To mitigate staffing shortages, the government is exploring partnerships with private sector firms and leveraging technology.
Private Sector Involvement
- Contracting external security experts for temporary staffing.
- Collaborating with tech firms for AI-based monitoring systems.
- Offering incentives to attract experienced professionals back to government roles.
Technological Solutions
- AI and Automation: Implementing AI-driven monitoring systems to enhance safety.
- Advanced Training Programs: Utilizing virtual reality (VR) for training new personnel.
- Data Analytics: Enhancing predictive maintenance through big data analysis.
Government’s Response and Future Steps

The US government is taking steps to address the staffing crisis and prevent similar issues in the future.
Proposed Solutions
- Improved Communication Channels: Establishing direct lines of communication with former employees.
- Better Employee Retention Strategies: Offering competitive salaries and job security.
- Expedited Rehiring Process: Streamlining security clearance and onboarding.
- Investment in Workforce Development: Enhancing training programs for nuclear safety professionals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Why were nuclear safety employees laid off?
The layoffs were part of a cost-cutting initiative aimed at reducing the federal workforce and reallocating resources.
How does this impact national security?
A shortage of nuclear safety personnel increases the risk of accidents, maintenance delays, and potential security threats.
Can laid-off employees return to their positions?
Yes, the government is attempting to rehire these workers, but challenges such as communication gaps and job market competition remain.
What is being done to address the staffing crisis?
The government is improving communication, expediting rehiring, and leveraging technology to mitigate the impact.
Are private companies involved in nuclear safety?
Yes, private firms are being contracted to fill gaps, and AI technology is being integrated to enhance monitoring.
How long will it take to restore the workforce?
It depends on the rehiring speed, clearance processes, and willingness of former employees to return.
What happens if nuclear safety staffing remains low?
Ongoing shortages could lead to security breaches, safety violations, and operational inefficiencies in nuclear facilities.
What lessons can be learned from this situation?
Better workforce planning, improved communication, and more potent retention strategies are crucial to preventing similar crises.
Conclusion
The government’s struggle to rehire nuclear safety personnel underscores the critical importance of strategic workforce planning. Atomic safety remains a top priority, and addressing staffing issues promptly is essential to maintaining national security. Moving forward, a combination of effective communication, technological advancements, and workforce incentives can help prevent similar challenges and ensure the safe management of nuclear materials.